Quick Start
This guide will walk you through the steps to add Skygear to your iOS project via CocoaPods from scratch.
Alternatively, you might want to get started with Skygear using:
Prerequisite
Step 1: Install CocoaPods
We recommend you to install the Skygear iOS SDK via CocoaPods. Run the following command in your terminal to install it.
$ sudo gem install cocoapods
Step 2: Install the Skygear iOS SDK
- Create a new Xcode project or use your existing one. Initiate pod if you have not.
cd your-project-directory
pod init
- Open
Podfileand add the following line to include SKYKit (Skygear iOS SDK) in your project.
pod 'SKYKit', '~> 1.1'
Note: It is not a must to specify the version number (i.e. 1.1). If you don't, your app will be using the latest SDK version automatically. Check out all the version numbers here.
- Lastly, run
pod installin your terminal.
pod install
- The Skygear iOS SDK will have been installed.
Step 3: Configure Skygear in your app
- In
AppDelegate.morAppDelegate.swift, import the Skygear iOS SDK.
-
Then add the following lines in the
application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptionsmethod to configure your app.- For Skygear iOS SDK with version 1.6.2 or before.
- For Skygear iOS SDK with version 1.6.3 or later.
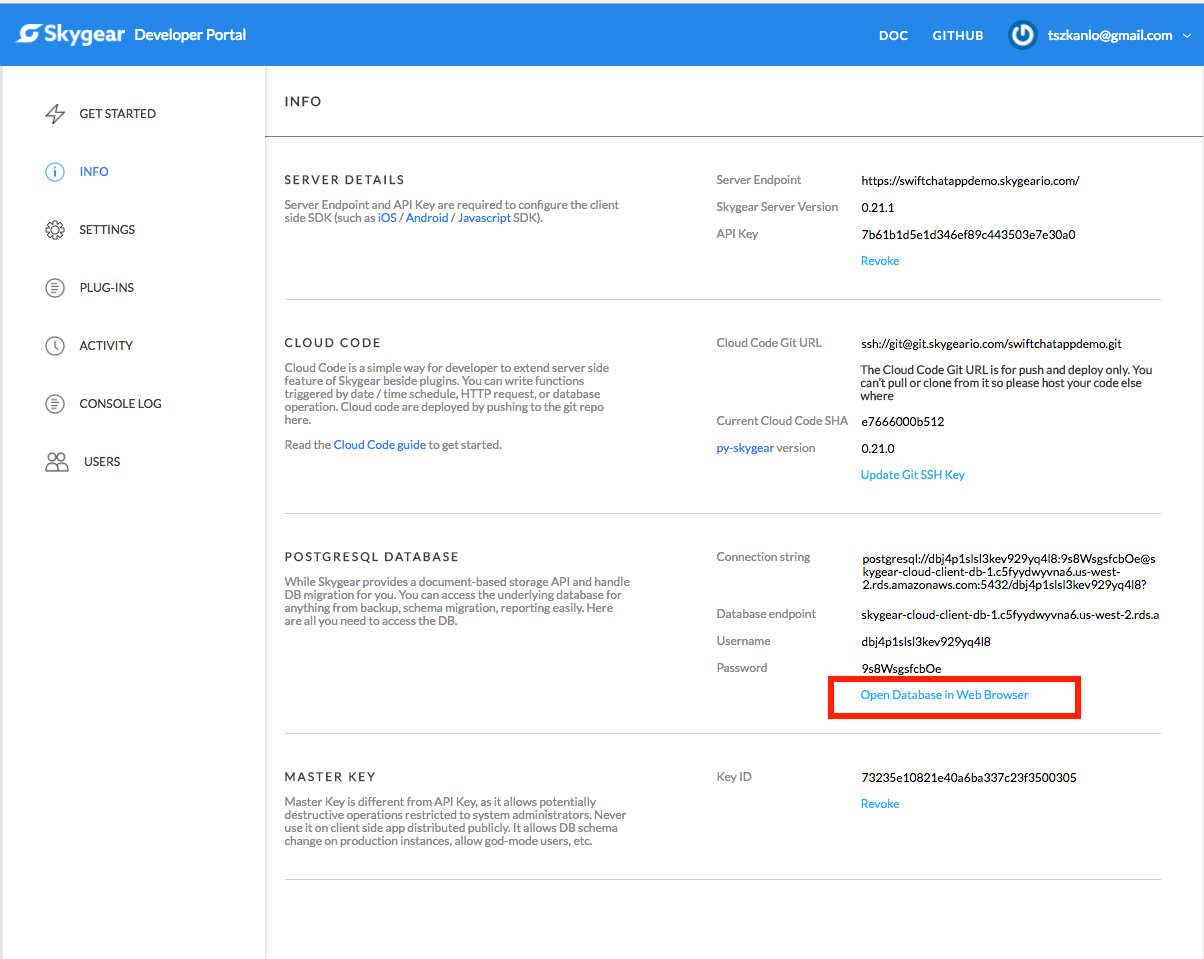
You can get your server endpoints and the API keys in the info page in your developer portal after signing up for the Skygear Cloud Services.
That is it. You are good to go now. You can continue with the step below to learn about basic database operations.
Step 4: Create your first record in Skygear
Now, let's create a record in the Skygear database to see if the SDK has been installed successfully.
Add the following lines in the application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions method and run your app in a simulator. The record will be created when you run your app.
Practically the codes should not be structured this way. It is for demo only.
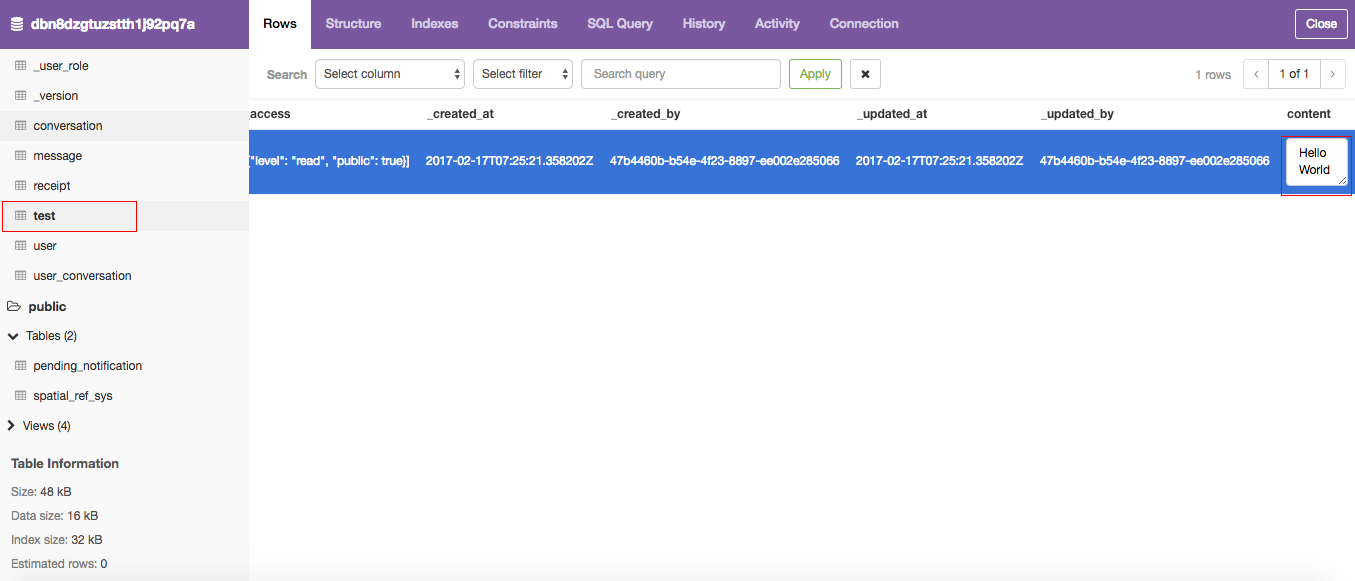
If the record is created successfully, you should see the record "Hello World" in your database table "test".
You can access your database using the data browser we provide. It can be found from the info page in your developer portal.
This is how your data browser will look like.
You can access Skygear database in 3 ways.
- Web data browser: It can be found from the info page in your developer portal.
- PostgreSQL client: Skygear database can viewed in any PostgreSQL client. Get the connection string from the info page in your developer portal. We recommend using Postico.
- Skygear CMS: Skygear CMS is a business-user friendly web interface that allows users to edit the data in the database. To use the CMS, you have to enable it in the plug-ins page in the developer portal. Your CMS URL is
https://insert-your-app-name.skygeario.com/cms.
Hurray! Everything should be in the right place from here.
What's next?
Next, you may want to learn more about: