Introduction and Deployment of Cloud Functions
What is Cloud Functions?
Cloud Functions are custom functions that run on the Skygear server. They are useful when:
- you need to build functionalities that are not basic database operations provided in the SDK
- you do not want to expose your codes in the front end client
On Skygear.io, you can also host static website for your apps with Cloud Functions.
Under the hood, Cloud Functions communicate with the Skygear server using a micro-services architecture through ZeroMQ or HTTP2.
Currently Skygear supports Python 3 and JavaScript for Cloud Functions.
Below is a simple Cloud Functions example, it will be triggered before a cat record is saved, and log an error if name was not filled.
Deploy Cloud Functions
skycli is the recommended way to deploy Skygear Cloud Functions.
skycli is the command line interface to Skygear Portal. You can use skycli to deploy your cloud functions to Skygear Cloud.
The recommended way to install skycli is via npm:
$ npm install -g skycli
You may also install skycli via Homebrew (macOS) as follows or download a binaries.
$ brew tap skygeario/tap
$ brew install skycli
You can run help to see the commands available at skycli:
$ skycli help
Authenticate in skycli
To init or deploy using skycli, you need a Skygear account (sign up for free at Skygear Portal).
- Open your command line interface.
- Run
skycli login - You will be prompt your email and password.
- After logging in, you can then initialize or deploy your cloud code via skycli. The login session persist on your machine. If you want to switch to another account, you shall logout first.
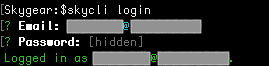
You can logout via skycli logout
Initialize a directory
You need to initialize a directory for a Skygear.io app endpoint before the deployment:
- Open your command line interface. Go to a directory for your project to init. e.g.
~/skyapp-cloud - Run
skycli init - Select an app - After confirmation on the project path, you will be asked which app to associate the local directory with. (You can create a new app on Skygear Portal)
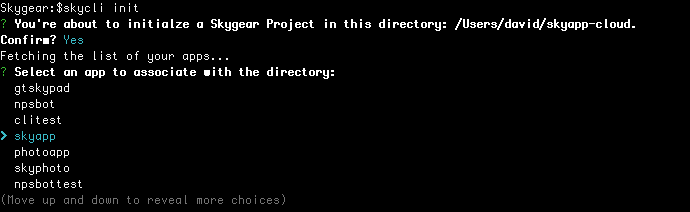
- Whether to create static hosting directory - Next, you can choose if you want to create your public static hosting directory. It is a directory for you to host assets or HTML files on Skygear.
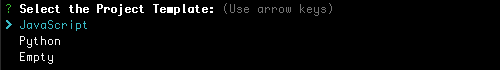
- Select your language - You will be prompted to choose use JavaScript or Python for your cloud code. A sample entry point will be set up (
index.jsfor JavaScript and__init__.pyfor Python).
- Completed! - skycli will then create files and configure your app info. You can start to write your Cloud Functions now.
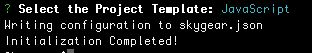
After skycli init, you will find a skygear.json in the root of project directory.
Deploy and upload Cloud Function
You can deploy by running skycli deploy in the directory initialized with a Skygear endpoint. You will see Build completed successfully. upon successful deployment.
If you prefer deploy and upload using git push, you can still upload your public key to Skygear
Portal via Manage Your Account, and git push to the master branch of
the ssh git endpoint at your developer portal Cloud Functions page.
How Cloud Functions Works
Now, let's examine the Cloud Functions example in details.
Functions defined in the Cloud Functions index.js or cloud_code.py are recognized by Skygear using decorators. There are 4 types of functions that
can be used; they are illustrated by the 4 functions in the examples.
1. Database Hooks
Database hooks can be used to intercept database-related API
requests. For example, you can use the before_save hook to perform data validation, or the after_delete hook to perform database clean-up tasks.
This example function will be called whenever a cat is saved
to the database, whether created or updated. When the new cat record
has an empty name attribute, it will raise an exception; and the
cat will not be saved.
More details can be found in Database Hooks.
2. Scheduled Tasks
Functions decorated with @skygear.every or skygearCloud.every are scheduled tasks that work similar to the cron daemon in UNIX: they will be run
by the Skygear Cloud at a certain time or in regular intervals.
This example function will run at two-minute intervals. You will be able to
see the log messages 'Meow Meow!' in the Console Log of your app in the Skygear Portal.
More details can be found in Scheduled Tasks.
3. Lambda Functions
Lambda Functions allow you to implement custom APIs, which can receive user-defined function arguments, and can be called from the SDK. They are useful when you need codes that are not exposed in the front end, e.g. connecting to a payment gateway to create transactions.
This example function creates a custom API food:buy, which
takes a food as the argument. The lambda function
can be called from the SDK, e.g. using skygear.lambda from JS.
const arguments = {'food': 'salmon'};
skygear.lambda('food:buy', arguments)
.then(response => {
console.log(response);
// {'success': true, 'food': 'salmon'}
})
.catch(err => {
console.error(err);
});
More details can be found in Lambda Functions.
4. HTTP Handlers
HTTP handlers can handle HTTP requests that are sent to the Skygear server through the specified URLs. They are useful when you need to listen to external requests like the webhook from a payment gateway service.
In this example, the HTTP handler is exposed through the URL
https://<your-end-point>.skygeario.com/cat/feed
as defined by cat:feed, accepting only GET requests.
It returns a response of the string 'Meow! Thanks!'.
More details can be found in HTTP Handlers.
Request Process Flowchart
The following flowchart summarizes the process for the Cloud Functions.